Project and Design Documentation
Contents
- 1 General
- 2 Architectural Goals
- 3 Requirements
- 4 Features and Functions
- 4.1 Internationalization
- 4.2 Reports
- 4.3 Graphs
- 4.4 Transaction Query
- 4.5 Simplified Ledger
- 4.6 Themes, Icons, Glitz
- 4.7 Miscellaneous Small Projects
- 4.8 Books, Accounting Periods
- 4.9 Check Printing
- 4.10 Wizards
- 4.11 Arrangements
- 4.12 User Preferences, Session Management
- 4.13 Architecture Review
- 4.14 Recurring Transactions, Calendar Alerts, Scheduled Transactions
- 4.15 Budgeting
- 4.16 Classes
- 4.17 Automated Test Suite
- 4.18 Quicken(TM) Import
- 4.19 IIF Import
- 4.20 IIF Export
- 4.21 Stock Quotes, Price Quotes
- 4.22 Install
- 4.23 Multiple Currencies
- 4.24 Forced Double-Entry
- 4.25 401(k), Retirement Savings Plans
- 4.26 Annotate with News Stories
- 4.27 Searchable Documentation
- 4.28 Reconcile Auditing
- 4.29 Loan and Mortgage Calculators
- 4.30 Overdraft Alerts
- 4.31 Technical Stock Analysis
- 4.32 Asset Depreciation, Sinking Funds, Amortization Schedules
- 4.33 OFX support
- 4.34 Other on-line support
- 4.35 Tab-delimited ASCII file format
- 4.36 Tax Preparation
- 4.37 Sync with Palm Pilot organizers
- 4.38 Emergency Records Organizer
- 4.39 Logging, Crash Recovery
- 4.40 Enriched Engine, Financial Objects
- 4.41 SQL I/O
- 4.42 Multi-user Support
- 4.43 Address Book
- 4.44 Accounts Payable, Receivable
- 4.45 Payroll
- 4.46 Invoicing
- 4.47 Order Entry
- 4.48 Job Costing
- 4.49 Expense Accounts
- 5 GnuCash Architecture
- 6 Decisions
- 7 Rules
General
The people behind GnuCash aim to create a world-class GPL'ed Open Source Personal Financial Application for GNU/Linux and other Unix's.
This page documents the technical issues and development directives surrounding this project. It is a kind of an FAQ for developers and contributors, providing status, and guidance.
If you simply want to get a better idea of what GnuCash is and what it does, visit its GnuCash home page or browse the GnuCash Wiki page. The home page contains screen shots, news items, and mailing list archives.
Architectural Goals
There are some over-reaching design principles and philosophies that we intend to maintain. Some of these concepts and terms are introduced in this section.
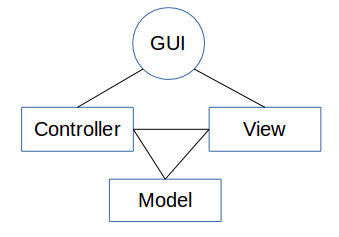
Separation of GUI and Data
First, we must maintain a clean separation between the data structures and the GUI that manipulates them, along the lines of the Model-View-Controller paradigm.
- Model
- Lists of accounts and the transactions in them can be thought of as a representation of financial data, a Model.
- Controller
- The GUI that adds, modifies and deletes these should be thought of as a manipulator of the data, a Controller. Thus, the Motif or Gnome GUI's are merely two possible manipulators of the data; others, based on e.g. web/cgi-bin, Qt/KDE, emacs, Java applets or Java servlets ought to be possible.
- View
- The View of the data is a subset or slice of the data described by the Model. The View may consist of only the transactions for the month of May, or only the account totals for certain accounts. The View is used in part to generate the reports and graphs, but it is also that which the Controller interacts with. Views are generated by queries to the data store.
GnuCash also needs to deal with multiple distributed datasources: stock quotations from the net or transaction confirmations from online banks and brokerage houses, or from more mundane sources, such as file imports, or merger of data from several users. Amongst these terms, the concept of a global Model-View is dated, and somewhat inappropriate. Rather, we need to be concerned about how data is represented in the local address space of the GUI, how the GUI manipulates it, how data is brought in and merged from external sources, and how that data is again output, whether to a file or a local or remote database.
Thus, the View essentially represents a local data cache of the data that is immediately present and being displayed, reported, and manipulated. The Model is the abstraction of that data that the GUI (the controller) can act on.
Financial Engine
In GnuCash, the Model is implemented via the Engine API, and the View is the data that is currently in the Engine. Thus, the Engine is a set of programming API's that the GUI (or a script, or even a clever command-line-addict) can use to manipulate the data.
Currently, the Engine provides basic accounting structures. These include:
- Transactions
- consist of a set of splits or journal entries (JE's) whose values sum to zero. The transaction includes several date fields, a description, and a common-currency field, and a universal unique id (uuid/guid). It also provides hooks to store arbitrary data associated with the transaction (using a URL-based key-value tree).
- Split
- (or journal entry) is an amount in the account on which it is drawn. Splits also store reconcile status, dates, a memo field, and also a key-value based hook for arbitrary data.
- Accounts
- include a name, a type, a description field, and the type of commodity they store. In principle, the account consists of a list of splits.
- Chart of Accounts
- is a hierarchical tree of accounts.
The Engine has a basic two-phase commit model, and a query mechanism for finding the data needed for reports and views. The goal of the two-phase commit and query model is allow the creation of multi-user server based backends, such as an SQL backend, and RPC client-server backend, or an XML-based HTTP/web backend. This design seems to work for the above-named backends.
The Engine currently handles only a basic set of data sources:
- It can import and merge in QIF's (actually, this function has been moved into the GUI, and is no longer part of the engine)
- It can read and write its own XML byte stream; This ability has been used to provide a multi-user client-server demo (which is currently broken).
- It can use a Postgress SQL database as a datastore, thereby enabling multi-user and auditing functions.
- It can talk, via RPC, to a GnuCash server. (This code is 'alpha' and incomplete/broken).
- It can get stock quotes from the net (actually, this function is provided by a separate module, the Finance::Quote perl module.)
However, since the Engine is meant to be the interface between the GUI and the financial data, it is really intended to be able to do much more. In particular, it should be possible to create a peer-to-peer network model, where GnuCash peers can synchronize data between themselves. The engine should also be expandable to handle other sources of data, such as OFX/IFX, the Open Trading Protocol, or the OMG CORBA General Ledger submission. In particular, it should be possible to use GnuCash not only to view data from these sources, but also to manipulate it and send it back.
Modularity, Extensibility and Customization
The above structure should lead us to view GnuCash not so much as a tightly integrated application, but rather as a loose confederation of component objects, libraries and interfaces. This has a number of advantages for both the developer and the user. For the developer, it allows parts to evolve semi-independently of one-another, and to be used in other, non-GnuCash projects. For the user, a good extensibility allows the use of #arrangements": a way of broadly customizing the appearance and behaviour of GnuCash, and then allowing users to very easily share these customizations with one another. Such arrangements might be collections of canned reports, e.g. for business or home user. Or they might be the menu contents: one menu arrangement is for beginners, another for 'power users', a third for business owners. The goal is that broad areas should be not only customizable, but it should be possible, even easy, to trade these customizations between users.
In order to facilitate the gluing together of these parts, as well as simplify the questions of customizability, change and rapid development, GnuCash makes use of the Scheme extension language (as implemented in the FSF Guile interpreter), to glue the pieces together. (Note that the engine interface is also available with Perl interfaces, thanks to a SWIG wrapper.
A Web Browser for Financial Data
More and more financial data is moving onto the web. People shop on-line. They pay bills on-line. There are even some promising e-wallet systems (such as WebFunds). For GnuCash to be relevant in this on-line world, it must be able to interact with these systems. There are several steps that can be taken along this path. First, it must be possible to simply and transparently import financial data off the web. Click on a QIF file, mime-type application/x-qif? GnuCash sucks it in without burping. But, in a more distant future, can GnuCash originate transactions? It should be able to!
GnuCash can be and should be "The Sophisticated Financial Web Browser". All GnuCash reports and the help system are HTML-based. In fact, GnuCash has a built-in web browser that can view ordinary web sites. Interactive GnuCash components such as the bar and pie charts, or the graphs and reports, can all be served up by a remote web server, as well as locally through the GnuCash application. This allows GnuCash to blur the line between web browser and financial application, and offer the best of both worlds.
Why is this a good thing? One can always have a pure web-based accounting solution (such as SQL-Ledger) that uses ordinary web browsers to view the financial data. But there are problems: dynamically-generated html and cgi-bins aren't as pretty or easy to use, or as fast, responsive or sophisticated, as what you can do with a custom client. That is, GnuCash can be more interactive, easier to user, slicker and more professional looking in style and presentation than a plain-old dynamic website. Financial ASP's simply cannot currently offer the kind of utility, flexibility, responsiveness and integration that GnuCash can offer.
In theory, the 'Java revolution' was supposed to provide this function, with downloadable Java applets providing the 'fancier- than-plain-html' interface. But a Java applet that is this sophisticated would also be large and slow to download: it offers no inherent advantages over native code. Another problem with Java is the inherent proprietary fragmentation: no two Java applets are alike: every site has their own; there is no standardization.
In order to solve the 'no gui standardization between websites' problem, there are a number of businesses that have arisen to provide "financial aggregation". You sign up with these sites, and let them get all of your credit-card, bank and investment info, and they can provide a unified interface for your bank statements, with graphs and reports (all for a monthly fee). The existence of these services highlights a problem: the inability to aggregate the same data on the users desktop, in a simple, coherent fashion. Let us posit that GnuCash, with the right on-line interfaces, would be a natural for this. For the paranoid, this has the added advantage that no one business has access to all of your financial records.
To put it another way, GnuCash can provide a centralized, trusted store for financial data that no other application can provide. The convenience factor: if you have trading accounts at e*trade and charles schwab, then GnuCash can be the central place where you can oversee all of your investments. The trust factor: maybe you can trust your web bank. Maybe you can trust your web stock account. But can you trust a single web entity with *all* of your financial data? Someone who won't treat you as 'just another consumer' and sell your 'consumer profile' to anyone who cares to stalk (ahem, target) your financial activity (ahem, purchasing) patterns? Didn't think so. Of course, you
- could* use some proprietary financial software. Assuming, of course, that you trust it not to have any built-in covert channels:
nothing that might send back the make and model of your CPU and the last ten transactions 'home to mommy' for 'diagnostic purposes'. Because open source software, such as GnuCash, can be audited it can be trusted in ways that no proprietary software can be. In an increasingly net-connected world, the ability to build trust through audits will be increasingly important.
Looking Into the Future
Things like support for OFX, and small-business features are hopefully in the near term future of GnuCash. Lets take a look at some more far-out possibilities.
- E-Wallet
- An e-wallet, just like a real wallet, stores cash. You can use that cash to pay friends or businesses. Just like a real wallet, an e-wallet should not charge you monthly fees. It should provide you with some measure of anonymity and privacy. An e-wallet should also do something no ordinary wallet can do: show you a monthly report of expenditures. GnuCash should get e-wallet features.
- Authentication, Authorization and Access Control
- How does an on-line merchant know that you are who you say you are? How can you use GnuCash to authorize a bill payment? Sooner or later, smart-cards will provide the sort of authentication and access control that is only groped for with PGP/GPG, keyrings, x.509 certificates, and Microsoft Passport/Hailstorm. Of all the electronic things in the electronic world where access control and authentication are important, real money is the most so.
- Bill Presentment, Bill Pay
- These magic keywords just mean that a merchant wants to send you a bill, and wants you to go to their website to pay that bill (they want your eyeballs). Of course, for the user, it would be more convenient to have the bill show up on the desktop, inside of GnuCash, and get authenticated and paid out from the desktop (by GnuCash), as you would do with all of your other bills.
Requirements
Lets take a look at who the current and potential future users of GnuCash are, and how they might use it.
The classes:
- Basic Household Accounting/Budgeting
- Personal Stock Portfolio Management
- Personal On-line Trading (Day-Trading)
- On-line shopping and bill-pay
- Small Business Users
These different applications may use some of the same financial terminology, and hopefully might share a fair bit of code, but have quite different goals and requirements.
- Basic Household Accounting and Budgeting
Important properties of a personal finance system include:
- Approachable and usable by occasional users who are not knowledgeable about accounting.
- Ease of use and simplicity is critical.
- A reasonable selection of reports, graphs, charts, and tools for personal finance, such as mortgage calculations.
- Budgeting support needs to be targeted at native users.
- Interfaces to on-line banking, shopping, stock systems. Bank and credit-card statements should arrive 'automatically' and always be up-to-date.
- Personal Portfolio Management
- Support for management of stock portfolios that may involve considerable sophistication, since individuals commonly have retirement plans that hold mutual funds, stocks, options, bonds, and the like.
- Reporting infrastructure needs to simplify handling of tax issues (long-term vs. short-term capital gains/losses, cost-basis FIFO accounting, simplified cost-basis spinoff/merger handling). Need on-line updates of prices, simple portfolio overview, ability to link to websites for additional research.
- Integration with on-line trading systems. This could save time typing.
- Basic Audit features. There's a problem with blindly allowing on-line data (prices, transactions) to enter GnuCash. It may not be clear where it came from, and even if the source is believed to be 'reputable', there still may be factual errors in the data. Thus, there must be a way of auditing newly-arrived (or even old) on-line data, and mark it as 'reconciled', i.e. manually reviewed and checked for accuracy. That is, incoming on-line data must be auditable, and audit trails should mark the history of on-line data import.
- Small Business Needs
- With a business system, it is likely that there will be users who use it eight hours a day, which puts the emphasis on efficiency of user interface rather than on its approachability to naïve users.
- Business systems require network support, and the ability to support multiple simultaneous users.
- Some business users may want access to the system from an MS Windows 95/98/NT box. For these folks, a web-based interface could be just handy. Web interfaces are also nice a for ASP type deployment.
- Small businesses do not often have sophisticated investment portfolios; they instead need support for additional sophistication in such areas as:
- Customer and Vendor Lists; Invoicing
- Payroll (Batch processed and individual)
- Inventory Control & Asset Management
- Amortization Schedules, Depreciation
- Shipping and Receiving
- Accounts Receivable, Accounts Payable (A/R, A/P)
- Credit Card Processing
- Support for calculations associated with accrual accounting.
- Ambitions for the future might include interfaces to online shopping carts, credit card clearing interfaces, and ERP systems.
- Reconciling Those Needs
A seemingly contradictory factor is that the kinds of sophistication that are required vary considerably. Consider:
- A home user does not generally require most of the sophistication of accrual accounting that is required by business enterprises. Thus, home users don't need much of the sophistication of an Accounts Receivable or Payable system, or the bizarre depreciation policies that crop up in Asset Management systems.
- On the other hand, home users are in increasing need of surprisingly sophisticated financial tools for managing stock portfolios, including:
- Mutual funds
- Retirement savings plans, with such identifiers as 401(k), IRA, Roth IRA, RRSP, or Insurance Annuities
- Corporate stock purchase plans
- Corporate option plans
Another set of contradictory requirements has to do with the back-end, and interfacing to other systems:
- Home users need a simple-to-install, simple-to-maintain system. This essentially rules out the use of SQL for the storage medium/back-end for home users. (That is, the current state of the art for SQL on Linux does not offer any simple, fool-proof management for data).
- By contrast, non-SQL systems for business use are almost unimaginable. SQL provides a high degree of data integrity and storage robustness, and also simplifies tremendously the import and export of data. Powerful SQL tools exist that can work magic in the hands of a good DB admin.
It may be that these will require completely different systems, and that GnuCash cannot be "all things to all people." This remains to be seen.
Features and Functions
This section reviews the current status of various features. Some of these are 'in process', some are 'almost done', some are 'completely done'. This section thus provides status on both where we've been, and where we're going.
Internationalization
All menus, markup and help-text should be internationalized, so that GnuCash may be usable in any country. This would include the printing of currency values in the local country conventions.
- Status
Essentially Done (?)
- All GUI messages currently use GNU gettext() for the message catalogues. Translations exist for English, British, French, Swedish, German, Japanese.
- Help pages available only in English and French.
- Monetary and string handling done through glibc. The latest glibc (2.2.3) is needed to get the correct functions.
- Yannick Le Ny <y-le-ny@ifrance.com> traduction en francais
- Most GUI input elements use the gtk text widget, and thus use the XIM input method in Asian locales. This allows e.g. Kanji, Katakana support. However, the register does not use XIM, and thus doesn't currently support the
Asian languages. This needs fixing. (This may be done already??)
Reports
A variety of reports, including Net Worth, Balance Sheets, and Profit and Loss statements. These should be printable: that is, exportable as HTML as well as print-ready postscript. These should be easy to customize. Ideally, even novice users should be able to create custom reports.
The Report Generator should be a separate but "dockable" subsystem of the whole. That is, it should be possible to run the report generator in a stand-alone, read-only fashion without having to start up the main application. It should be possible to run reports nightly from a command-line and/or cron job. The GUI should remember what reports were run last time, and these should be re-run/redisplayed whenever the report generator is used.
One difficult aspect of reporting is designing a configurable interface, so that people can build custom reports. The New Reporting Infrastructure is seeking to build this up using Guile. Note there are several flavours of customization:
- Allow user to specify a custom logo (e.g. company logo/address) on every page (generically, having a header and footer for every page).
- Allowing user to modify report title/subtitle on the fly (and possibly add notes at the top or bottom of the report, e.g. to explain line items).
- Allow user to use the transaction query interface to pick the set of transactions that will make up the report.
- Memorize the report that was asked for, give that report a name, and in the future, allow that same exact report to be re-run. Allow user to edit this report properties at a later date. Note that the basic idea is similar to that of memorized queries, discussed below.
- Design Notes
- Note that the customization info should be stored in an Arrangements File (see below).
Generated reports should be exportable to other gnome systems (probably using bonobo). Reports should also be exportable to the Gnumeric spreadsheet (probably by writing out gnumeric file format). Export of CSV (comma separated values) and tab-delimited formats (for other spreadsheet import) would be good. Tables & etc. should be exportable to AbiWord, StarOffice, other word processors. (formats: docbook sgml? would then make convert to richtext, TeX easy.) Export should be as wysiwyg as possible.
Must be possible to e-mail reports (for example, invoices) to users. Suggest an evolution addressbook /mailer bonobo plugin.
Relationship to budgeting not clear ...
Stock portfolio tools should include a Cost Averaging report, Market Index report, Stock Option values, Estimation of capital gains tax liabilities.
Reports should be printable to printer (postscript/ Adobe Acrobat).
- Status
- A general reporting infrastructure was implemented in Perl, in the form of html-embedded perl (ePerl). However, this reporting mechanism was abandoned in part because ongoing build and install problems related to ePerl and swig. Also, since ePerl didn't participate in the interpreter even loop, the report generator had to run as a separate process, reading data via pipes. This was uglier than some folks liked.
- A general reporting infrastructure has been implemented in Scheme. Currently, there are a variety of reports for Profit/Loss, Balance Sheet, and portfolio valuation; none are particularly sophisticated.
- Done: Reports are displayed with the gtk-html widget. This widget provides postscript printing and Acrobat output.
- There is currently no way (no longer any way??) to generate reports from the command line ...
- While many reports have been implemented, there is no master list of what we should have. We should have ....
- The following technologies were rejected/unused mostly because they were too complex, didn't hang together technologies: SGML and Extensible Markup Language - XML. In the long run, these are preferable to HTML, since DSSSL tools such as Jade (James DSSSL Engine) can be used to convert to RTF, Postscript, etc. Add to this the consideration that XML is the basis for the Document Object Model, which is being integrated into many web-based applications, and we can see that XML is an increasingly significant format as we look to the future.
Graphs
Provide support for graphs, charts, etc., such as: Asset allocation pie chart, portfolio value vs. cost, ROI. Graphs should be printable to printer. Graph generation should be fully integrated with reporting, both for data collection via queries, and for displayed output.
- Status
- Currently jqplot is being used for generating graphs. While it has the potential for interaction (click-through) this is not implemented.
- Basic pie charts and bar charts are used in GnuCash reports. There are problems: dates along the bottom of a bar-chart are not well-spaced/autoscaled. The over look is a bit clunky.
Transaction Query
Allow user to build (complex) queries to locate a set of transactions that match some criteria: e.g. a date range, or a matching payee, description, amount, etc. Once a user has created a complex query, it must be possible to memorize it (i.e. give it a name, and store it for future reuse).
- Status
- The query engine has been implemented (as of 1.4.0, grib)
- The GUI for creating queries has been implemented (as of 1.4.0, grib)
- The queries are handled by the Postgres SQL backend. (as of 1.6.0, linas)
- Queries can be turned into XML and back, for file storage or network transmission. This used to work for XML version 1 but was broken in version 2.
- The ability to memorize queries has not been implemented and awaits further action (needed for reports, above).
Simplified Ledger
Ledger should look clean, work easily.
- Status
Essentially done.
- Multi-line ledger confusion fixed by using correct left-right journal display style. Fixed in 1.6.0, Peticolas, Champaigne.
- Stocks and Mutual funds are handled by placing them each in their own account. Each account can be viewed individually. If all of the stock accounts are children of a master trading account, then the trading account can be viewed and modified in a General Ledger window. Layout problems fixed in 1.6.0.
- How to most simply allow the user to enter loads and fees? Through multi-line transactions. Seems to work well in 1.6.0.
Themes, Icons, Glitz
A variety of finer touches need work:
- Hint-of-the-Day A collection of a some 50-100 hints-of-the-day: short (2-4 sentence) hints/tips on how to use GnuCash. Every time the user starts GnuCash, an new hint shows up ... Status: Hint infrastructure complete (RGMerkel, version 1.4.0). Need to add hints (only a dozen are currently available).
- Themes Some theme testing required. The effect of themes on the register window needs to be reviewed. Some themes look flaky in the main account window, might be a gtk bug ???
- Household Assets/House Inventory Add wizard to walk user through a set of questions about household inventory & help user value them. (do you own a house? appraised value? mortgage? do you own jewellery? appraised value? etc.) In particular, show how appreciation and depreciation should be treated. See the section Arrangements for a discussion of the customization issues.
- More account types Introduce more 'fundamental' account types: (amortized) Loan, Mortgage, ESOP, House, Line of Credit.
- Register View Allow user to view only non-reconciled transactions ...
- Configurable main-window Status Bar Bottom of main window currently shows total asset, and total income-expense (profits). Make this configurable, so that user can show arbitrary sums of arbitrary accounts. This is mostly solved by having the MDI interface have reports, and the use of multi-panning. But the default display for GnuCash should be changed to show a very small (1-4 line) networth and P&L report, and maybe a cash-flow report. See the section Arrangements for a discussion of the customization issues.
- Dockable Registers/ aka "Browser Mode" Currently, when each new register opens, it opens in a new window. An alternate style would be to 'dock' the register window in a bigger frame, and just have 'backward/forward' buttons to navigate through different registers (the way that a browser navigates web pages.) This of course would be a user preference. Possibility for doing this exists with MDI. Maybe we shouldn't bother doing this ??
- Context sensitive help When users create new accounts, need to suggest stuff if the user typed something unexpected ... (e.g. non-alphanumeric input) ...
- Folder Tabs Currently, Income/Expense accounts can be shown or hidden by selecting from a menu. It would be nice to be able to examine different account types (Asset, Liability, Income, Expense, Payables, Receivables, Inventory) by selecting a tab folder. This is maybe a bs. request that shouldn't be implemented.
The following have been completed, but possibly not fully documented:
- Pop-up Calendar All date fields should pop up a calendar widget; selected date should get entered in field. (peticolas, version 1.4 ??)
- Pop-up Calculator All price/amount fields should pop up a calculator widget; output of calculator gets entered in field. Instead of a popup calculator, this was implemented by allowing all fields to take algebraic expressions (plus, minus, times, divide). (rlb ?? version 1.6.0)
- Button Bar A user-configurable button-bar. Solved in version 1.6.0 with tabs, not buttons, via gnome MDI (gribble, version 1.6.0) See also the section Arrangements for a discussion of the customization issues.
- Currency Exchange Table Keep a currency exchange-rate table. This is now automatically handled via the 'price database' (rlbrowning, version 1.6.0) (the finance::quote perl module handles currency exchange rate fetches)
- Currency Selection Pop-up Currency field should get replaced by menu of long-hand currency names, three-letter ISO 4217 abbreviations, and symbols. User should be able to hand-enter non-IS4217 currencies. Status : Done in 1.4.0
- Cut-n-paste Cut-n-paste of whole transactions in the register window... Status: Done in 1.4.0, Dave Peticolas
- Auto-completion Quick-fill should also auto-complete amount, memo fields. Status: Done in 1.4.0, Dave Peticolas
- Autoincrement Check numbers should auto-increment. Hit + key in check number field (same keystroke as in quicken). Status: Done in 1.4.0, Dave Peticolas
- Navigation Menu navigation using the keyboard should be possible. Hit the Alt-F to get file menu, hit Alt-FS to save. Similarly, tab-key navigation in the register should be possible. Status: Done (in 1.3.x ?, Dave & all, partly inherited via gtk widget set.).
- Fly-Over Help When the user pauses the mouse over a button, "fly-over" pop-up help windows should appear. Status: Done (in 1.3.x, inherited via gnome/gtk widget set).
- Grayed-out Form Help Create grayed out entries in the ledger, titled "Memo", "Description", etc, helping users understand what should be typed into each field. Status: Done (by Dave?), as of version 1.3.2(?)
- Key Bindings for Editing Text Fields The input fields use the gtk text widget, which provides key bindings that are similar to the Netscape/emacs key bindings. This allows e.g. emacs-style ctrl-a, ctrl-k to do the right thing. Status: Done (in 1.3.x, inherited via gnome/gtk text widget).
Miscellaneous Small Projects
A variety of small internal projects. All have been completed as of 1.6.0
- File Format Rework to use text file format. Will be XML-based. Status: RLB, LewisMoss. Version 1.6.0 Done.
- Reconcile Window Auto-pay credit card when reconciling credit card accounts (Done, Dave). Auto-add bank fee when reconciling bank accounts. (Not done?, Dave).
- Print Register Window Output register window to printer. Status: Done: there is a register report which is printable, there is bottom on register. Done in 1.6.0
- # of decimal places in prices (penny stock) Part of the big numeric overhaul. Done, Gribble, others, version 1.6.0
- gtkhtml Move to gtkhtml from gtk-xmhtml. Done in 1.5, Grib.
- print Print reports, etc. Done in 1.5, Grib. This came 'for free' with gtkhtml.
- key-val pairs Add generic key-slot mechanism into accounts, transactions, journal-entries. Done in 1.5.0, Grib.
- guid in fileio No longer relevant with new file format. Dave.
Books, Accounting Periods
Ability to close the book at end of the fiscal year. This consists of several steps:
- Permanently lock some transactions as non-editable. This should be straight-forward by using the reconciled field to indicate a locked value, and not allowing the GUI to edit locked records.
- Transfer the Income minus Expense for the book period to an equity account, so that each new period starts with zero income/expense balances.
- A mechanism to purge really old transactions from the database.
- Extensions to querying and reporting infrastructure ... The query changes might be painful ...
- A user should be allowed to 'delete' an account only if it has no transactions in the currently open book. Of course, it's not deleted from the old books. From this last, we conclude that every chart of accounts should have a beginning and ending date (that match the book period), and the file format needs to support multiple charts ...
- Memorized Transactions ... Currently, transaction auto-completion works by auto-completing with the last 'similar' transaction. This ability will get trashed when books for the old year get closed, because there won't be 'similar' transactions.
- Status
- A mini-design Doc exists in src/engine/extensions.txt A far more extensive, four-part proposal is ??? somewhere in the mailing list archives (by Linas Vepstas, circa Feb-May 2001)
Check Printing
Create a check-printing ability. Include MICR (Magnetic Ink, Computer Readable) check printing abilities. Yahoo Check Printing provides a list of vendors & printers.
Print vendor/client/payee address on the check (so that check can be mailed with window envelopes.) This requires GnuCash to integrate with addressbook.
- Status
- More check formats need to be supported.
- Done, except for address part, in version 1.4.0. (gribble)
- Need a sample check/sample transaction to print out so that user can test printer.
- MICR Fonts are available & brought to mailing list.
Wizards
Create a set of wizards to walk through some of the more complex tasks, such as new user setup, account creation, QIF import, budget prep, obscure functional corners.
Wizards are great, but lets not throw away the denser GUI's. For 8-hour-a-day users, the wizards can be irritating. A single, dense screen can be more efficient and nicer. So when adding wizards, don't dump GUI's !! (instead, make them 'advanced' features).
- Status
The following not done:
- Account Creation The account creation panel is somewhat busy. Maybe could use a wizard?
- Budget Setup Setting up a budget.
- Obscure Corners Various obscure corners of the application may be non-intuitive, and need wizard help. e.g. stock splits? e.g. using foreign currency on a business trip?
- Completed
- New User Setup Provide a default Chart of Accounts, which will mostly consist of a default set of 'Categories' (Income/Expense Accounts). These are categories such as "Automobile Expense", "Bank Interest Income", and "Employment Income". The user should be able to select a default set of accounts, and have those created automatically. Profiles: home-owner vs. renter non-for-profit (some non-profits are very very simple, just a club). Done in version 1.6.0, C. Champagne, J LewisMoss
- QIF Import QIF Import is just complicated enough that it needs a wizard walk-through of the steps. Grib, version 1.6.0, Done.
Arrangements
An "application arrangement" is the defining look-n-feel of an application. The idea is similar to, but not the same as 'skins'/'themes'. Its similar to, but not the same as allowing a user to set 'preferences'. Its similar to, but not the same as, allowing a user to generate customized financial reports. In the context of GnuCash, a 'arrangement' should be a file (that can be traded by users, uploaded and shared) that controls important aspects of how the application is configured.
In particular, the GnuCash Arrangement should include the following:
- A list of sample/initial accounts. These might be tailored for a home user (groceries, gas, electric), an apartment dweller (rent, laundry), or different kinds of business users. Because these sample accounts appear in the Arrangement file, it becomes easy to create & distribute customized arrangements.
- A list of pre-defined reports and graphs. The kind that you'd find for a home user might be different than for a person managing a stock portfolio, which is in turn different from what a business might need. The Arrangement File should include install-specific customizations, such as the report headers, footers, etc.
- Hint of the day. The types of 'hint of the day' would be different for new users, than it would be for advanced users. Thus, different arrangements would have different catalogues of 'hint of the day'.
- Menu Contents & Navigation. New users might be presented with a simple set of menu contents. 'Power Users' might be presented with deep, nested sets of menus, with oodles of features.
- Register Layout. The layout of the register might be customized for different countries: e.g. in Germany, a different type of electronic banking seems to require the display of account numbers in separate columns in the register.
- Design Notes
- A good arrangement infrastructure will not only allow GnuCash to be configured for different application domains, but also will allow users to fine-tune their own preferred arrangement. It can also simplify the code base: instead of having two products, a home-user application, and a small-business application, each with a different code base and #defines and what not, instead, we have one code base, and different arrangements for each. However, most importantly, the arrangements should be easy to share between users. They should be such that users are encouraged to trade and use arrangements, and to create new ones that suit their needs. The idea for arrangements was inspired by Adam Curry's commentary on radio formats and Napster.
- Status
Not started. Individually, all these customizable things exist here and there in GnuCash, but they cannot be shared between users: a GnuCash user cannot mail her favourite 'arrangement' to her freind.
User Preferences, Session Management
A dialog system and file format for manipulating user preferences. Preferences include things like default currency, register layout and colors, etc.
What are some of the competitive preference-handling technologies? Lets get some URL's here ... Following the Unix tradition, there is no global preferences registry. Note that session management and preferences are related things ... sort-of. Right now, we don't treat them as such ...
- Status
Done, more or less, version 1.6.0.
- Works real good; lots of preferences in the GUI. Implemented in home-grown scheme. (version 1.4.0, rlb)
- These are saved in the '.GnuCash/config.auto' file. The current file format is raw scheme code, rather delicate to tweak by hand ...
- Session management mostly works, but doesn't use the sawmill/gnome/X ICCCM system. GnuCash remembers MDI based reports, restart reopens in same state. Sizes and shapes and positions are remembered. Done in version 1.6.0
- Independently of session management, the register windows should remember how big they were last time they were popped up, and they should pop up the same size, again. The app should remember these sizes from invocation to invocation. Done in version 1.6.0, but seems a bit buggy.
Architecture Review
The application is wired together partly with C, partly with Scheme. The architecture of the wiring and how scheme is fit in needs to be reviewed, with a general overview created so that additional extensions may be added in a straightforward manner.
The overall architecture is envisioned thus: All code, including the transaction engine, the file I/O routines, the menus, and the ledger, will be abstracted into compact modules that can function independently of each other. At the highest level, there will be a infrastructure with extension language interfaces that will "wire together" the various modules.
Such "wiring together" will consist of a dispatch infrastructure that will allow arbitrary menu entries to be hooked to arbitrary modules. The configuration for menu entries, and their associated callbacks, will be specified in an extension-language configuration file. At the final stages, it is highly desirable to be able to, in some manner, import new modules without requiring that the application itself be recompiled and relinked.
- Status
- Scheme/Guile is the central extension language. Guile interfaces auto-generated using swig.
- Optional interfaces to the data engine (for, e.g. python) can be generated using SWIG.
- Dave to collate & edit architecture documents. RLB to provide diagrams.
Recurring Transactions, Calendar Alerts, Scheduled Transactions
- Add support for automatic, recurring transactions, e.g. mortgage payments, fixed-interest bonds, regular salary checks, regular gas/phone/electric bills, etc.
- Recurring bills, salary income, etc. are simpler to handle, since they don't have interest rates, balloons, etc. They do/will have multiple splits (e.g. payroll gross, fica, futa, income taxes, payroll net).
- Provide list of upcoming & recently paid bills/scheduled payments/scheduled deposits for the next 1,2,3,6,12 months. Historical view shows payments crossed out (!?)
- Loans & mortgages are one of the more complicated recurring transactions. Typically, there might be a years worth of smaller payments, then a long string of larger payments, followed by a balloon.
- Provide a calendar-display of upcoming & past scheduled payments. Clicking on a calendar day should raise up editable list of transactions. Calendaring should include generic red-lettering of important dates: taxes due, insurance renewal dates, domain registration renewal dates, ISP contract expiration date :-). These may or may not be associated with transactions. Memo's should be possible. Pop-ups should happen when dates get close. Technology: best bet is the Ximian Evolution Calendar component.
- Design Notes
- Most alerts & data storage should be driven out of the engine. This will enable multi-user, distributed use. Note: alerts should be piggy-backed on a general alert infrastructure within the engine, viz, registered callbacks when balances change, so that windows can be redrawn. Not clear on if/how calendar events might be server-ified. (On the other hand, a good calendar should be server-ified, and thus viewable by secretaries, co-workers, etc.)
More complex financial instruments may need a guile-based extension mechanism to compute values .... simple interest/mortgage calculators should be done in C in the engine ... (e.g. depreciation schedules ... under us tax law, a variety of different schedules are allowed ... )
May need interfaces to email for emailed alerts.
Plot forecast graphs based on scheduled income & payments ... is this tied into budgeting ????
- Status
- Need to create design doc, need to implement engine pieces, need to hunt down gnome-calendaring bonobo.
- Preliminary work started.
Budgeting
Ability to create a budget (i.e. - estimates of future expenditures). Reconcile actual expenditures against future expenditures. Create simple, step-by-step 'financial plan' budgeting GUI's:
- Home purchase planner
- Retirement planner
- College tuition planner
- Debt reduction planner
- Scrimp-n-Save planner
- Special purchase planner (big ticket items)
- Design Notes
- Create a summary budget/track-record budget report that a professional financial planner/advisor could use.
Note that the above 'step-by-step' budgeters will have a very very different GUI than what the budgeting system required for a small-business might look like.
Note that the utility of budgets is greatly enhanced by using them with 'classes'.
- Status
- A design doc has been submitted by Bob Drzyzgula. Take a look at ./src/budget.txt in the source directory.
- Bryan Larsen has begun work .. it's scheme based ... Dave Peticolas has some GUI roughed out ...
Classes
- Design Notes
- Ability to mark certain journal entries as belonging to a 'class', so that expenses (or income) can be categorized in more than one way. For example, the expense of a trip might include food, travel and lodging, and thus be spread over three different expense accounts. None-the-less, we want all of these entries to be marked as being in the same class.
Alternate names: 'job costing' is the report that's generated, 'cost center', 'cost pool', 'pooling')
Note that classes can be particularly useful when used with budgets: viz. I set aside $10K in the budget for some activity, then deduct the actual costs. Note that it should be possible to roll the remainder over to somewhere else (!)
Confusion: isn't this what the 'action' field is supposed to do? The 'action' field is under-utilized.
This requires the following:
- Ability to report by class/action
- Ability to query by class/action.
Automated Test Suite
Build automated test suite, including:
- File IO consistency check. Done, 1.6.0, LewisMoss
- Currency math correctness. Done ?? Grib.
Quicken(TM) Import
- Design Notes
- Ability to import Quicken QIF files. Both MSMoney and Quicken use QIF files to export data. Need both wholesale data import, and incremental (staged) merge.
- Status
- Quicken import is implemented and mostly works. (Bill Gribble, Done, in version 1.4.0)
- Need a QIF Import wizard (there are several non-intuitive steps that need to be performed during import. A dialogue wizard seems like the best idea to carry through this process. (grib, done in 1.6.0)
- Work needs to be done for recurring transactions, etc.
- QIF processing, as used for on-line banking, is in prototype form (for 1.6.1 ??) Note that since banks use QIF, the correct way to updated 'cleared' reconcile state is through QIF on-line import. On one side, we have existing recorded transactions; on the other, the latest bank statement, in QIF format.
IIF Import
Ability to import IIF (Intuit Interchange Format, used by Quickbooks) files, quickbooks, some upscale accounting packages use this format.
- Status
- Sample files checked into sample directory. No formal documentation known.
IIF Export
Ability to export Intuit IIF files. The IIF format is more rational than the QIF format, and other 'real' accounting apps support IIF. Several design alternatives are apparent: A special 'report' that writes out qif could be created. This would use the 'reports' infrastructure to generate QIF's. It is fairly easy to traverse the data in the engine to write out qif files. This is not hard. Just do it.
- Status
not started
Stock Quotes, Price Quotes
Add ability to obtain stock, mutual fund, and currency trading data from news agencies, web pages. Add ability to download historical prices as well. (e.g. get 5-year history of mutual fund performance vs. DJIA).
Right now, stock prices are stored in a separate, simple pricedb.
- Prices need to have several different status states. One state is 'critical/audited', i.e. reviewed by a human, and important for understanding a historical transaction. Less important may simply be 'audited': i.e. reviewed by a human, but not a critical price. Lowest level: 'live data' something that was gotten off the net, may be wrong, may be right, who knows, who cares.
- Add to this the idea that we should probably store other 'technical' stock data, such as share volume, high/low/close, daily volatility, etc.
- Need access to historical quotes, for graphing charting of historic portfolio performance.
- Status
- Finance::Quote.pm is now a separate development project at SourceForge. Its a perl module. It can obtain stock quotes from Yahoo (NYSE), Yahoo-Europe, Fidelity Investments, T.Rowe Price, TIAA-CREF, others. Also handles currency exchange rates.
- A scheme wrapper allows prices to be fetched from GUI. Done, version 1.6.0, rlbrowning.
- Commandline-flag replaces script file gnc-prices perl script). Suitable for use with cron jobs. (version 1.6.0)
- A separate, historical-quote module can be found at the QuoteHist sourceforge site. It might be a good idea to fold this together with the Quote.pm module !?
Install
- Design Notes
- Install on Redhat, Caldera, Corel, SuSE, FreeBSD, TurboLinux, etc. Possibly use a 'configure'-like way of dealing with install inconsistencies.
- Status
Flatpak is available since 3.9.
Multiple Currencies
Need to support multiple currencies. Work is needed in the GUI. The engine currently supports multiple currencies by treating them as securities, thus allowing currency trading. The currency-trading register needs a complete overhaul as it is obtuse and unintuitive. Weird stuff is in weird columns.
A simplified way of dealing with one-shot currency exchanges needs to be implemented, essentially just a simple calculator pop-up. This might be handy for the occasional business traveller or tourist with some minor currency trades.
Implement the 'correct' way of handling this when user is working in multiple currencies on a regular basis.
SERIFF Simple Exchange Rate Information File Format. Completely *.ini-centric in layout and design, but otherwise seemingly quite complete.
- Status
- Need to rethink whether the one-shot exchanges should in fact be recorded full-fledged in the engine. Also: Euro support is currently hacked in: the EURO is treated as a 'special' currency. Virtually all the Euro code can be fully generalized (and should be).
- New split architecture should store quantity and value, and never the price. This will simplify currency movements between accounts, without requiring/forcing the use of a currency trading account. (this also solves problems with rounding that occur when a price is explicitly specified.) Grib & dave are working this for next release.
Forced Double-Entry
The system supports double-entry: every transaction indicates a pair of accounts: one is debited, and one is credited.
Double-entry is a powerful way of ensuring the integrity of of the financial data. Currently, while double-entry is supported, its use is not enforced: the user can create dangling transactions, where only one account is indicated.
Although this is acceptable for home use (arguably desirable, since it allows the casual user the simplicity they desire), it is not acceptable for business use. (The counterargument is that casual users that aren't accountants need all the help at getting things right that they can get.)
It must be possible to enforce double entry, so that a transaction cannot be completed until two accounts have been specified.
Restricted Double Note that sometimes, the words 'single-entry' have a an alternate meaning: they can mean 'a double entry account which can only be credited, or debited, but not both'. We need to implement this.
- Status
- April 1998 -- The engine has a couple of flags in it that control double-entry behaviour: it can be made lax or strict, however, they are compiled in, and there is no way to change them from the GUI.
- Dec 1998 -- Scrubber functions implemented to crawl through data, and find all unbalanced or orphaned transactions.
- May 2000 -- Default will be changed to double-entry always. It will not be possible to disable this and move to single-entry.
401(k), Retirement Savings Plans
401K, 403, IRA, Roth IRA, SEP, Keogh ... Retirement Savings Plans often do not put a high priority on tracking costs, as the tax implication is that amounts are taxable upon withdrawal, meaning that there is little necessity to track capital gains. (huh??)
Annotate with News Stories
Download, save, annotate investment news and research. Provide a way of storing news stories with accounts, and possibly annotating individual transactions in the same way.
Searchable Documentation
Need to add a 'meta keyword' tag to the documentation pages, this will help the search engine (e.g. htdig) better categorize the help. Mifluz might be more embeddable ... I am told that htdig-API is in good solid condition for this, but undocumented.
- Status
Done, using a simple keyword search, homegrown. The only problem is it doesn't support compound expressions.
Reconcile Auditing
When a collection of transactions get processed through the reconcile dialogue, user needs to be able to add a note to this, i.e. this set of JE's will be treated as a group. The note (and date) can be later called up as a part of an audit procedure. The act of reconciliation is created as a historical event that needs to be logged.
Loan and Mortgage Calculators
Provide a variety of simple GUI utilities to allow user to calculate the future value of loans, mortgage payments, interest payments, etc.
Consider the following dialogue layout:
loan amount $_____________ currency _________ (pull-down menu) Remaining balance $___________ Payment amount $___________ balloon payment $_____________ other payment $________ (e.g. escrow, tax) Payment frequency (weekly/monthly/bimonthly/quarterly/yearly) loan start date mm/dd/yy length -----(weeks/months/years/payments) loan time left (number of days/weeks/months, rounded) number of payments left interest rate %__________________ payee ____________ pay-from account __________________ next due date mm/dd/yy
Note that in the above, not all fields are independent: some can be calculated from others. The other payment should bring up a mini-register, allowing user to add any number of splits.
- Status
There is an implementation of the calculation routines by Terry Boldt in the development branch. There is an initial GUI implementation of the calculator by Dave.
Overdraft Alerts
Overdraft alerts are pop-ups that pop up whenever the user enters a transaction that would move an account below some minimum balance, or above some max balance (for a bank account) or an expense/spending limit is reached (on an expense account). A similar but different alert can be implemented for price highs & lows. Note that these alerts do not require any sort of calendaring or recurring transaction support.
Design requirements: implement multiple (not just two) alerts for any account type. Alert should consist of:
- value point or price point
- movement direction
- 'is active' Boolean flag (i.e. Should be possible to 'turn off alert' without deleting it)
- memo text
- Status
- Not Started.
Technical Stock Analysis
Provide technical stock analysis graphs, e.g. volume, 90 moving avg, beta, etc. See gstalker for example of how to do it ...
Asset Depreciation, Sinking Funds, Amortization Schedules
Need to support different depreciation schedules (see IRS books for that). Asset depreciation is complex; there are many different depreciation schedules, and these vary from country to country, and change when new tax laws are implemented. It might be hard for free software to provide a no-cost subscription to updated depreciation modules.
OFX support
Provide the SGML DTD parsers to handle the OFX reports that many banking institutions are providing, or will soon be providing, to retail customers. See below for OFX references.
OFX is an open spec from Microsoft, Intuit, and Checkfree, and which will be supported by Integrion. The OFX DTD's are included in the 1.1 distributions. See OFX Home Page for details.
There are two ways to build an OFX parser. One way is to build a compile-time DTD parser that treats the DTD as if it were an IDL, and generates C language stubs for a parser. This approach was attempted and abandoned because it leads to fragile C code and a very large binary.
- The parser is fragile because minor DTD non-compliances are hard to parse, handle and recover from.
- The parser is huge because the DTD results in hundreds of (C++) objects being generated.
- Design Notes
- The other method would be to perform run-time DTD parsing. This is attractive particularly because it is a more commonly-used approach; there are a variety of XML tools available that provide this function.
Run-time parsing may be slower, but on the OFX client side, this should not be a bottleneck.
- Status
- A compile-time parser was developed and abandoned.
Note that the organizations developing OFX are looking to use XML as their "formats of the future;" this may encourage the use of one of the many XML parsers available for UNIX.
Other on-line support
>> the German T-Online >> homebanking system BTX. >> >> I Germany we have a very popular online homebanking system, >> based on the T-Online BTX (Datex-J) system. All of the >> commercial homebanking software packages like MS-Money or >> Quicken work with that online system. With that system, >> you can retrieve account data from your bank, and also >> send your transfers. >> >> I am using since more than 2 years a GPL software written >> by a former colleague of mine, Niek Busscher, to work with >> the T-Online homebanking system. That software package with >> the name ZKA4BTX is very unknown, since Niek published it only >> by email. >> >> Some words to the features of ZKA4BTX : >> >> - Completely written in Tcl >> - Uses Xcept as a BTX browser >> - Retrieve account data from multiple banks >> - Send transfers, using TAN >> - Export retrieved account data to CBB, Xfinans and QIF files >> - Export retrieved account data to CBB, Xfinans and QIF files >> >> With a simple click to an icon on my desktop, ZKA4BTX logs into >> T-Online, gets all my account datas from several banks, and writes >> (adds) it to my CBB, Xfinans or GnuCash (QIF) files. >> >> Another very important thing is that I can do all my transfers >> offline, editing a transfer sheet, and ZKA4BTX sends these >> transfers in one step to my bank. > >One thing we could do in the short-medium term is have GnuCash >launch ZKA4BTX to get the data, export it to QIF, and then load >it in, all through one command.
Tab-delimited ASCII file format
People like to be able to read file contents in ASCII; there are many Unix tools for manipulating ASCII. An ASCII equivalent of the current file format should be easy to develop ... just substitute the writes with printf()s.
The tab-delimited format should be compatible with that of /rdb, aka RAND/Hobbs /rdb or NoSQL. (NoSQL is available as part of the distribution, for instance.)
The /rdb format is thus:
field-name tab fieldname tab fieldname \n ------------------------------------------ \n value tab value tab value \n value tab value tab value \n etc ...
It is a very simple, very basic flat table format. The use of /rdb with GnuCash should try to match with SQL schemas as much as possible in order to minimize I/O complexity and incompatibility.
Tax Preparation
Gotta prepare those taxes. W-2, W-3, 941, 940 Processing.
- TurboTax -- categorize items according to different tax schedules
- VAT -- Value Added Tax. Varies from country to country.
- Estimate income taxes. Estimate itemized deductions, find potential deductions, categorize them
Sync with Palm Pilot organizers
There are Quicken-workalikes that run on the PalmComputing platform; it would be good to inter-operate with this. See PalmLink and Palm & Linux.
Emergency Records Organizer
Put together a single-page report showing critical info about accounts, etc.
Logging, Crash Recovery
Logging serves two purposes: (1) return the system to the state it was in on some earlier date. (2) recover from a crash. Probably need two distinct mechanisms to support this. The mechanisms are (A) backup copies. These can be compactly handled via RCS (actually, deltax) for storage. (B) Logging. Write out to disk each & every change made.
- Status
- Crude transaction logging/auditing in place; should be suitable for error/crash recovery but has not been "tried by fire".
- Backup files automatically created and time-stamped.
Enriched Engine, Financial Objects
The current system makes a distinction between the data (account, transaction) and they GUI that displays it. The data is embedded within and controlled by the "Engine", which is a set of routines to access accounts, transactions, etc. The engine serves as a kind of a dynamic cache between the permanent data repository (file, sql db) and the GUI.
The current engine is rather simple: it provides support for accounts, account hierarchies and transactions consisting of multiple entries.
Many of the features described elsewhere will require that the engine have a far richer, more sophisticated data model, including such things as:
- Linking to "Address Info" ( e.g. names, addresses)
- Transaction identifiers
- Part numbers, SKU IDs
- Interest rates
- Budget policy
Note: it makes no sense at this point to make the engine API much richer than what the GUI can currently support.
- Locks When splits are implemented, and the parent transaction has been marked as cleared/reconciled, the record should be locked, so that further modifications to the amount can't be performed (or at least, a warning is generated to prevent accidental garbaging up of old transactions).
- Status
- BeginEdit()/RollbackEdit()/CommitEdit() routines mostly in place, these "Transaction processing constructs" should simplify creation of an SQL back end, or some other more sophisticated transactional server.
- Multiple currency support is present but still pretty "raw."
- Query engine has been broadly extended (Bill Gribble). Documentation for Query Engine??
SQL I/O
A module is necessary to allow data to be fetched from an SQL database, and for that database to be updated. There has been much discussion about this on mailing lists both for GnuCash and CBB. Major points have included:
- The use of a database allows only that data which is actually in use to be loaded into memory. This permits managing larger sets of transactions more efficiently.
- It also allows data to be pushed out to the DBMS immediately after entry, rather than waiting for the user to "save the books."
- Using a client/server SQL database might make it easier to turn GnuCash into a multi-user system.
- By using a well-known DBMS, outside programs are provided a well-defined way of getting at, and perhaps even modifying, GnuCash data. (Actually, this is not true: GnuCash already provides a uniform, well-documented, preferred data access API. As long as this API is used, there is some guarantee that data is stored in a self-consistent fashion. Not using the GnuCash programming interfaces risks corrupting the data. Direct access to the data is dangerous and discouraged. Furthermore, The API is guaranteed to be backwards compatible with a variety of data storage formats. Due to enhancements, the actual form of the data stored in a flat file, or in the SQL database, may change without warning.)
- Those SQL databases available on Linux tend to involve considerable administrative overhead in terms of getting them set up. This may be a minor cost to a business enterprise that routinely hires Database Administrators. It is not acceptable to require this of naïve users that may find "simple" things like
% su - Password: # cd /tmp # rpm -i GnuCash-4.1.3.i386.rpm # exit
to be challenging.
- It might be useful to use an embedded database engine like unto Sleepycat DB, cdb, or something like ISAM (Note CQL++ supports ISAM access methods), or even an embedded SQL engine such as GigaBASE. The reasons to do so include ... ???
- GnuCash presently uses a document-oriented model, where the entire set of books are loaded in, and dumped out, all at one fell swoop. GnuCash needs to be modified to access the database in a transactional manner. This is at least partly implemented with the Begin()/End() constructs in the engine.
- Some transactional thoughts: entire SQL tables/databases do not need to be locked while the user is editing a transaction via the GUI. Instead, an optimistic approach, similar to that employed by CVS (concurrent version system, a mechanism for storing versions of source code) could be used: if the edits conflict with changes made by others, edits are be rejected en-masse, allowing the user to merge and correct their changes. Important note: updating SQL does not require locks to be held for extended periods of time!
- The SQL engine chosen should be fully transactional, passing the 'ACID' test (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability). Note that MySQL does not satisfy the 'ACID' criteria.
- Status
Done, more or less, GnuCash version 1.6.0, Linas Vepstas. There's still a laundry list of things that need to be cleaned up, see the README file in src/engine/sql/README.
Multi-user Support
Multi-user support should be added with either an SQL backend to the engine, and/or through CORBA interfaces to the engine. Another possibility is to create a web application server, and have users do much/most of I/O via a web interface, possibly using the register object as a browser plugin. The following industrial-strength features are needed:
- transaction-oriented queuing of updates
- event subscription channel for updates
- user authentication
- user authorization
- non-reputability (needed only for peer-to-peer??)
- encryption of network connections
- Status
Partly done. (GnuCash 1.6.0, Linas) The postgres backend fully supports multiple simultaneous users. This includes events for automatic updates of all GUI displays. However, the GUI support is rough, no GUI dialog for user/password.
Address Book
Provide support for client/vendor/customer address books, including street address, email, phone. Also: to-do lists, a mini-contact manager (when is last time this person was paid? what did they say on phone the last time we sent them a check? Is there a dispute?)
Propose: use Ximian Evolution contact manager/to-do lists.
Accounts Payable, Receivable
Add features to track sales receipts and other pending sources of income, as well as owed sums.
- Need new account type 'ar' and 'ap'. When this account type is selected, the register display, etc. is slightly different, as below:
- Add field to register called 'date due'. The date could be entered as 'date of transaction +30days'. etc. The account could have a default: entries always default to +30 or +45 days or whatever.
- Create a report to match 'date due' to current date, and report overdue balances ...
- Create Account aging report: show (average) age of amount-due/amount-owed.
- Create a projected cash flow report: showing projected future payments based on date due.
- Somehow, automatically match invoices to payments. When an invoice has been paid off, then there should be a view mode where the invoice and its payment is no longer shown (i.e. so that only outstanding, unpaid entries are shown ...)
- create report showing everything but the a/p: Here's an example. I buy a chair for a friend, and three days later he pays me back. What I've been doing is ...
> 1/12/01 Credit -$100 > A/R +$100 > 1/15/01 Cash +$100 > A/R -$100
To make it less painful to read and understand, the report should look like:
> 1/12/01 Credit -$100 > 1/15/01 Cash +$100
i.e. there would be a new kind of 'transaction report' that would pair up transactions in this way, showing things 'as if' the A/R didn't exist, and 'as if' a transaction was spread over a bunch of days.
Payroll
Payroll introduces a sizable amount of complexity in terms of the need to comply with constantly-changing government regulations in whatever country one is in. While the GnuCash "engine" might remain free, maintenance of payroll functionality would require "subscribing" to an update scheme; it might be troublesome to try to provide such a "subscription" free of charge.
Invoicing
Invoicing. Note that invoicing and order entry are closely related. Several components:
- Record an invoice. Assign it a serial number. Be able to reprint/report based on invoice serial number.
- Invoice associates customer name to set of transactions. Need to deal with PIM issue. I.e. need to integrate with high-function PIM or CRM interface.
- Allow historical browsing of invoices customer by customer.
- To visually design an invoice, need to have a mini-word-processor/simple drawing plug-in. Is Abisource/Abiword a candidate? Probably needs bonobo...
Order Entry
Mini-GUI allowing users to type in orders.
- Should interface to parts/inventory database to confirm item availability, (maybe recommend additional production)? inventory should be updated after order placement.
- Automatically update accounts receivable.
- Allow order revision/update (esp. as partial orders are shipped).
- Orders can be invoiced when entered (simple invoicing), or placed on account (double invoicing).
- Allow back-orders to be printed customer-by-customer, or by product/item.
- Allow printing of packing slip.
Job Costing
Ability to prepare and track estimates.
- Allow estimate/bid to be converted to a firm order & get invoiced.
Expense Accounts
Expense Account Automation, including air, car, hotel, dining. Receipts, reservations, cancellations.
GnuCash Architecture
Introduction
GnuCash is designed with the goal of a clean separation between the data structures and the GUI that manipulates them, along the lines of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) paradigm. Unfortunately, only parts of the application's building blocks really stick to this separation, but we will outline this goal below anyway and will point out the difference between the current status and the long-term goal. The interaction of the MVC components are coordinated by some instance that might have been called the engine, but in the current status there is no single instance that is responsible for this coordination.
- Model
The Model concept is the abstraction of that data that the user can act on. Lists of accounts and the transactions in them can be thought of as a model representation of financial data. Current Status: However, there is no single place in GnuCash where the relevant data structures of "the model" are defined. The majority of this data abstraction is defined within the modules "src/libqof" and "src/engine", but clearly those modules contain also parts that represent the controller concept and even a little bit of the view concept.
- View
The View is a presentation of a data subset or slice of the data accessible in the Model. The View may consist of only the transactions for the month of May, or only the account totals for certain accounts. The View is used in part to generate the reports and graphs, but it is also that which the Controller interacts with. Views are generated by queries to the data store. Thus, the View essentially represents a local data cache of the data that is immediately present and being displayed, reported, and manipulated.
- Controller
The GUI that adds, modifies and deletes these should be thought of as a manipulator of the data, is a Controller. Thus, the Gnome GUI or some other GUI are merely two possible manipulators of the data; others, based on e.g. python or Qt ought to be possible. The controller is allowed not only to act on the data presented by the view, it may also modify the view e.g. by sending certain filter or sorting requests to the view.